NGP Inc.
12778 rue Clearview
Pierrefonds Quebec H9A1B5
(514)999-2008
support@ngpeng.com
Recovering from Noise the Response of Fiber Optic Sensors
Recovering from Noise the Response of Fiber Optic Sensors We work currently on an interrogator for fiber optic sensors targeted mainly to bare single mode optical fiber used as distributed fiber optic sensor. External perturbations such as local force or temperature change applied to optical fiber induce non uniformity in the refractive index of fiber core which produce backward propagating Brillouin scattering. Brillouin signals can be very weak, sometimes hidden in optical fiber noise. The magnitude of Brillouin signal is proportional with the magnitude of the external perturbation. There are available commercial equipments which can detect Brillouin signals up to 40Km far from interrogator if these signals are well above the noise level. It will be very useful to depict small external perturbations which generate weak Brillouin scattered photons named later response or signal, comparable with noise level or less than this. The use of such small signals will increase the sensitivity of bare optical fiber used as sensor.
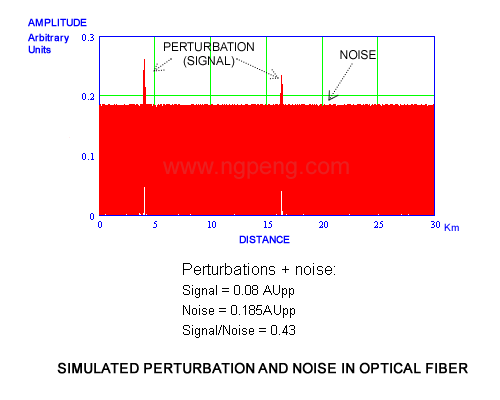
We developed an approach for recovering from noise Brillouin signals which can be even below noise level. The Simulated Perturbation and Noise in Optical Fiber graph shows a situation when one fiber response is below the noise level, such as Signal=0.08, Noise=0.185, or Signal/Noise (S/N)=0.43. The numbers on vertical axis show the signal strength in arbitrary units or AU. The horizontal axis of the graph shows the distance from the interrogator to the current point in Km.
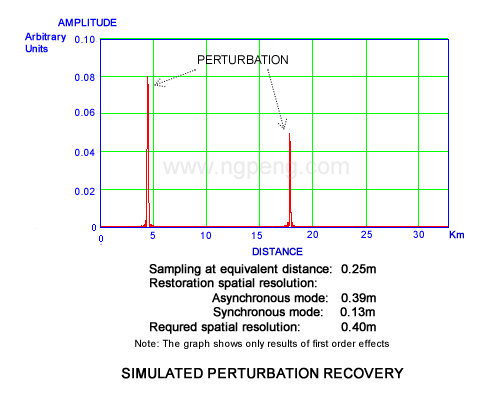
Using our approach of recovering sensor response from noise, we simulated the recovery of Brillouin signals generated at about 16Km far from the interrogator, as you see in Simulated Perturbation Recovery graph below. Note that this graph shows the simplified case of first order effects.
We focus now our efforts for reliable detection of back scattered Brillouin signals coming from external mechanical perturbation of several microstrain.